Are Teeth Bones? Understanding the Differences and Similarities
Have you ever wondered, “Are teeth bones?” It’s a common question and one that puzzles many people. While teeth and bones have some similarities, they are different. This blog post will explore the materials that make up teeth and bones, their differences and similarities, and how to care for them. You’ll clearly understand their unique roles in our bodies by the end.
- What Are Teeth Made Of?
- What Are Bones Made Of?
- Differences Between Teeth and Bones
- Similarities Between Teeth and Bones
- The Importance of Teeth and Bones in Our Bodies
- How to Take Care of Your Teeth
- Proper Brushing Technique
- How to Take Care of Your Bones
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions - Are Teeth Bones?
What Are Teeth Made Of?
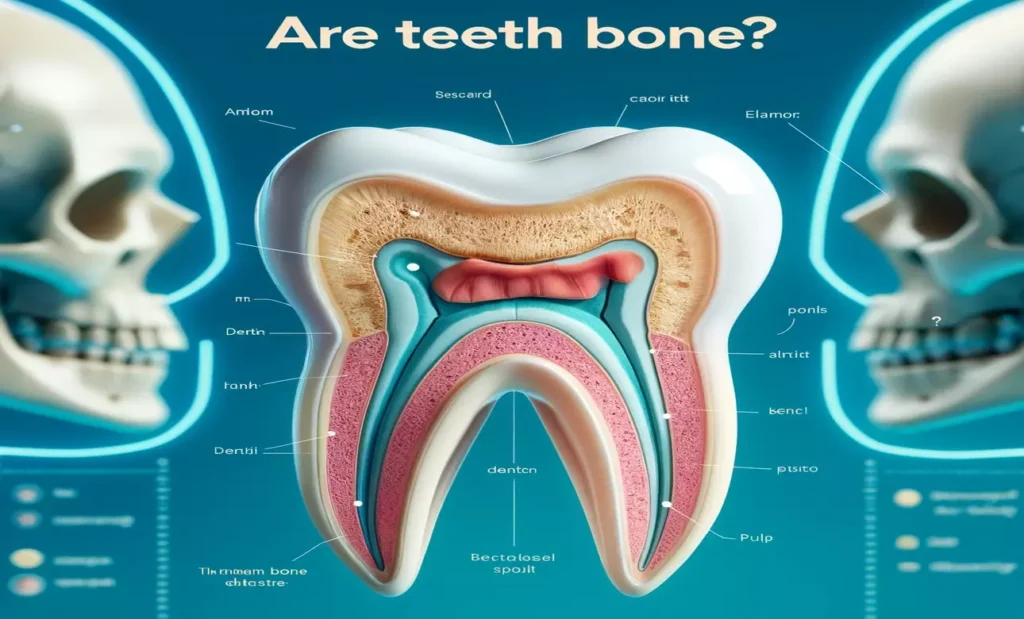
Teeth might look like bones, but they are made of different materials. Here’s what makes up a tooth:
Enamel: This is the tooth’s tough, white exterior. Enamel is the toughest substance in the human body, surpassing even bone in strength.
Dentin: Under the enamel is dentin, a yellowish layer that is softer than enamel but still harder than bone. It reinforces the enamel and helps absorb some of the pressure during chewing.
Pulp: Inside the tooth is the pulp, which has nerves and blood vessels that nourish the tooth. It represents the living tissue of the tooth.
Cementum: This layer covers the tooth’s root and helps anchor it to the jawbone.
What Are Bones Made Of?
Bones are vital parts of our body structure. They consist of multiple elements:
Collagen: This protein provides a soft framework for the bones.
Calcium Phosphate: This mineral adds strength and hardens the bones.
Bone Marrow: Inside many bones is bone marrow, which produces blood cells.
Periosteum: A dense layer that covers the outside of the bones, providing a surface for muscles to attach.
Differences Between Teeth and Bones
Though they might seem similar at first glance, teeth and bones have several key differences:
Composition: Teeth are mostly made of enamel and dentin, while bones are made of collagen and calcium phosphate.
Living Tissue: Bones are living tissues that can heal themselves. They contain marrow, which produces blood cells. Teeth, however, do not heal themselves. Once enamel is harmed, it cannot be restored.
Blood Supply: Bones have good blood supply. Teeth have blood vessels only in the pulp, and the enamel and dentin are not supplied with blood.
Function: Bones support and protect various body organs, store calcium, and help with movement. Teeth are primarily for biting, chewing, and speaking.
Similarities Between Teeth and Bones
Despite their differences, teeth and bones also share some similarities:
Hardness: Both are among the most complex substances in the body.
Mineral Content: Both contain calcium, which helps them stay strong and stiff.
Support: Teeth and bones support our body structure. Teeth help us chew food, and bones help us move and protect our organs.
The Importance of Teeth and Bones in Our Bodies
Teeth and bones are crucial for various bodily functions:
Teeth: They help us chew food, which is the first step in digestion. They also help us speak clearly and give shape to our faces.
Bones: They provide structure and support for the body. Bones protect our internal organs, store and release fats and minerals, and produce blood cells.
How to Take Care of Your Teeth
Caring for teeth is essential to avoid problems like cavities and gum disease. Here are some tips to help you maintain excellent oral hygiene and ensure your teeth stay strong and healthy.
Brush Twice a Day
Brushing your teeth twice a day is one of the most essential practices. Use a fluoride and a soft-bristled toothbrush. Brushing for at least two minutes each time removes food particles and plaque that cause tooth decay and gum disease. Give particular focus to every surface of your teeth: the front, back, and chewing areas.
Floss Daily
Flossing is essential for removing plaque and food debris from spaces between teeth that a toothbrush cannot reach. This helps prevent cavities and gum disease. Floss at least once daily, ideally before going to bed.
How to Floss Properly:
- First, take approximately 18 inches of dental floss. Then, wrap the majority of the floss into middle fingers, leaving 1 to 2 inches of the floss available for use.
- Gently enter the floss between your teeth and carefully move it up and down along the sides of every tooth.
- Wrap the floss around the base of each tooth, making sure to go below the gum line.
Visit the Dentist Regularly
Arrange to see your dentist at least twice a year for routine cleanings and examinations. These visits help identify early signs of dental issues, such as cavities, gum disease, or oral cancer, enabling timely treatment.
Benefits of Regular Dental Visits:
- Professional cleanings eliminate tartar that regular brushing and flossing may miss.
- Early detection of cavities and gum disease.
- Personalized advice for improving your dental hygiene routine.
- Screening for oral cancer and other health conditions.
Eat a Healthy Diet
To help prevent cavities, it’s best to avoid sugary foods and drinks. Maintain a balanced diet, as this is crucial for keeping your teeth and gums healthy. Instead, concentrate on consuming foods rich in calcium and phosphorus, which help strengthen teeth. Dairy products, leafy green vegetables, nuts, and lean proteins are excellent choices.
Teeth-Friendly Foods
Dairy Products: Dairy products including cheese, yogurt and malik are good sources of calcium and vitamin D.
Leafy Greens: Spinach and kale provide essential vitamins and nutrients.
Crunchy Fruits and Vegetables: Apples, carrots, and celery help clean your teeth as you eat and stimulate saliva production, which neutralizes acids.
Avoid Tobacco
Using tobacco products, whether smoking or chewing, can result in serious dental problems such as gum disease, tooth loss, and oral cancer. Tobacco use may also lead to bad breath and tooth stains, impacting overall appearance and oral health.
Why You Should Quit Tobacco
- Minimizes the risk of gum disease and oral cancer.
- Enhances the look of your teeth and refreshes your breath.
- Enhances your sense of taste and smell.
- Overall improvement in your general health.
Additional Tips for Dental Care
Use Mouthwash: Use antibacterial mouthwash to avoid plaque, prevent gum disease, and maintain fresh breath. Look for a mouthwash with fluoride for added protection against tooth decay.
Drink Plenty of Water: Water aids in washing away food particles and bacteria, and staying hydrated supports saliva production, which is essential for a healthy mouth.
Avoid Teeth-Staining Foods and Drinks: Limit your intake of coffee, tea, red wine, and foods with intense pigments. If you consume these, rinse your mouth with water afterward to minimize staining.
Wear a Mouthguard: Wear a mouthguard while playing sports or grinding your teeth at night, as it can protect your teeth from damage.
Following these comprehensive dental care tips can help you maintain a bright, healthy smile and prevent common dental issues. Practice good oral hygiene as it’s a lifelong commitment that rewards you with robust, healthy teeth and gums.
Proper Brushing Technique
Properly brushing your teeth is essential for maintaining good oral hygiene and preventing issues like cavities, gum disease, and bad breath. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to properly brush your teeth to ensure they remain clean and healthy.
Step-by-Step Guide to Brushing Your Teeth
Choose the Right Toothbrush
Soft-Bristled Brush: A toothbrush with soft bristles does not harm your gums and enamel and is effective at cleaning your teeth.
Size: Select a toothbrush that fits comfortably in your mouth and allows you to reach all areas easily. For children, choose a smaller-sized toothbrush designed for their age group.
Use Fluoride Toothpaste
Fluoride: This mineral aids in reinforcing tooth enamel and helps prevent cavities.
Amount: For adults, a pea-sized amount of toothpaste is adequate. For children under 6, use a smaller, rice-sized amount to prevent excessive fluoride ingestion.
Angle Your Toothbrush
Holding the toothbrush at a 45-degree angle to your gums allows the bristles to effectively access and clean the gum line, where plaque tends to accumulate.
Brush All Surfaces
Outer Surfaces: Clean the outer surfaces of both your upper and lower teeth using light, circular motions for a comprehensive clean.
Inner Surfaces: Tilt your brush vertically and use up-and-down strokes to clean the inner surfaces of your teeth
Chewing Surfaces: Brush your teeth chewing surfaces using a back-and-forth motion. These surfaces can harbor food particles and plaque, so thorough cleaning is essential.
Tongue and Roof of the Mouth: To freshen your breath and get rid of bacteria, softly brush your tongue and the palate of your mouth.
Brush for Two Minutes
Ensure you brush for at least two minutes by timing yourself.
Use Gentle Pressure
Apply gentle pressure while brushing. Brushing with excessive force can harm your enamel and cause irritation to your gums. Let the bristles do the work.
Don’t Forget the Gum Line
Gently brush along the gum line where your teeth meet your gums. Plaque tends to build up here, so cleaning this area thoroughly is essential.
Spit, Don’t Rinse
Spit out toothpaste after brushing, but avoid rinsing your mouth right away. Rinsing can wash away the fluoride, reducing its beneficial effects. If you like to rinse, opt for a fluoride mouthwash.
Additional Tips for Effective Brushing
Change Your Toothbrush Frequently: Swap out your toothbrush every three to four months or sooner if the bristles start to wear down.
Consider Electric Toothbrushes: Electric toothbrushes can be more effective at removing plaque and are often easier to use.
Choose a Toothbrush with a Comfortable Grip: Ensure the handle of the toothbrush is easy to hold and allows for easy maneuverability in your mouth.
Following these steps and brushing your teeth twice daily, you can maintain excellent oral hygiene, maintain good oral health, and keep your smile vibrant and healthy. Remember, proper brushing is just one part of a comprehensive oral care routine that includes flossing, mouthwash, and regular dental check-ups.
How to Take Care of Your Bones
Bone health is just as crucial as dental health. Strong bones support your body and protect your organs. Here’s how to maintain healthy bones:
• Balanced Diet: Consume diet that is high in calcium and vitamin D-rich foods. Leafy green vegetables, dairy products, and fish are excellent sources of calcium and vitamin D.
• Regular Exercise: Weight-bearing exercises, such as strength training, walking and running can help build and preserve bone density.
• Avoid Smoking and Limit Alcohol: Both can weaken bones and increase the risk of osteoporosis.
• Sunlight: Spend time outside to help your body produce vitamin D, essential for calcium absorption.
• Bone Density Tests: As you age, regular bone density tests can help detect osteoporosis early, allowing for timely treatment.
Conclusion
Teeth and bones might seem similar but fundamentally differ in structure and function. While teeth are not bones, both play vital roles in our health and daily activities. Understanding their differences and similarities helps us take better care of them. By following proper care routines and maintaining a healthy lifestyle, you can ensure the longevity and health of both your teeth and bones.
Frequently Asked Questions – Are Teeth Bones?
Are teeth stronger than bones?
Indeed, tooth enamel is tougher than bone, making it the hardest material in the human body.
Can teeth heal themselves like bones?
No, teeth cannot heal themselves. When enamel is harmed, it is unable to heal on its own. This is why it is essential to take good care of your teeth.
Why do we need both teeth and bones?
Teeth have a crucial role in chewing food and speaking clearly, while bones support our body, protect organs, and produce blood cells.
What should I eat to keep my teeth and bones healthy?
Have foods that are rich in vitamin D and calcium, like dairy products, leafy greens, and fish. Avoid sugary foods and drinks to protect your teeth from cavities.
How often should I visit the dentist?
Make sure to see your dentist at least twice a year for routine check-ups and cleanings.






