Best Edge Computers: Driving the Future of Distributed Computing
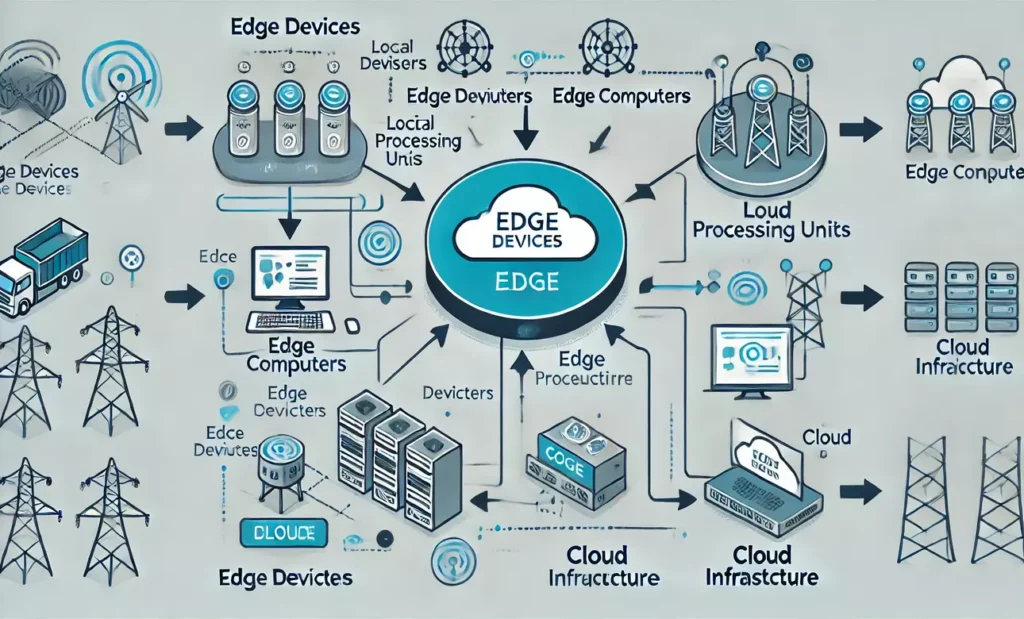
Edge computing has become a groundbreaking technology by enabling data processing and analysis to occur nearer to where the data is generated. At the heart of this revolution are edge computers, specialized devices designed to handle the unique challenges of edge environments. This article explores the world of best edge computers, their applications, and the top options available today.
- Understanding Edge Computing and Edge Computers
- Key Features of Top Edge Computers
- Top 10 Best Edge Computers in 2024
- Edge Computers in Various Industries
- Edge Computing vs. Cloud Computing
- Challenges and Limitations of Edge Computing
- Addressing Edge Computing Challenges
- Future Trends in Edge Computing
- Choosing the Right Edge Computer
- Case Studies: Successful Edge Computer Implementations
- FAQs About Edge Computers
- Conclusion: The Future of Edge Computing
Understanding Edge Computing and Edge Computers
Edge computing operates as a distributed model that relocates computation and data storage closer to where they are needed. This approach reduces latency, conserves bandwidth, and enables real-time data processing.
Key characteristics of edge computing:
- Proximity to data sources
- Real-time processing capabilities
- Reduced network latency
- Enhanced privacy and security
- Bandwidth optimization
Edge computers are the hardware components that enable edge computing. These devices are designed to:
- Operate in resource-constrained environments
- Process data locally with low latency
- Handle AI and machine learning workloads
- Provide robust connectivity options
- Withstand harsh environmental conditions
Key Features of Top Edge Computers
When evaluating edge computers, several features stand out as crucial for optimal performance:
1. Processing Power
- Multi-core CPUs (e.g., Intel Core i7, AMD EPYC)
- GPU acceleration (e.g., NVIDIA RTX, AMD Radeon)
- AI accelerators (e.g., Google TPU, Intel Movidius)
2. Memory and Storage
- High-speed RAM ranging from 8GB to 64GB or more
- Fast storage options (NVMe SSDs, eMMC)
3. Connectivity
- Multiple Ethernet ports (1GbE, 10GbE)
- Wi-Fi 6 and 5G support
- Industrial protocols (Modbus, PROFINET)
4. Ruggedness
- Wide operating temperature range (-40°C to 85°C)
- Fanless designs for dust resistance
- Elevated IP ratings for protection against water and dust
5. Security Features
- Trusted Platform Module (TPM)
- Secure boot capabilities
- Hardware-based encryption
6. Power Efficiency
- Low-power consumption designs
- Support for wide input voltage ranges
7. Expandability
- PCIe expansion slots
- M.2 and mini-PCIe slots for additional functionality
Top 10 Best Edge Computers in 2024
1. NVIDIA Jetson Xavier NX
- Compact design with powerful AI capabilities
- 6-core NVIDIA Carmel ARM v8.2 64-bit processor
- 384-core NVIDIA Volta GPU featuring 48 Tensor Cores
- Provides up to 21 TOPS of AI performance
- Ideal for use in computer vision, natural language processing, and robotics applications
- Energy efficient (10-15W power consumption)
2. Google Coral Dev Board
- Designed specifically for edge AI applications
- Features Google’s Edge TPU for accelerated machine learning inference
- Supports TensorFlow Lite models
- Low power consumption
- Suitable for prototyping and small-scale deployments
3. Intel NUC (Next Unit of Computing)
- Compact yet powerful mini PC
- Multiple models featuring a range of Intel processors, from Core i3 to i7
- Supports Windows and Linux operating systems
- Suitable for edge computing, digital signage, and IoT gateways
- Customizable with various storage and memory configurations
4. Dell Edge Gateway 5200
- A durable and adaptable edge computer designed for industrial use
- Features Intel Core i5 processors
- Up to 32GB of RAM
- Multiple I/O options
- Designed for harsh environments
5. HPE Edgeline EL8000
- High-performance edge computer for demanding AI and analytics workloads
- Accommodates up to four Intel Xeon Scalable processors
- NVIDIA Tesla GPU support
- Ideal for data-intensive applications
6. Lenovo ThinkSystem SE350
- Compact yet powerful edge server
- Intel Xeon D processors
- Up to 256GB of RAM
- Enterprise-class performance in a rugged design
7. AWS DeepLens
- Designed for computer vision applications at the edge
- Integrated with AWS services for easy deployment of ML models
- 4MP camera with 1080P video
- Intel Atom processor
8. Advantech MIC-770
- Industrial-grade edge computer
- 9th Gen Intel Core processors
- Multiple expansion slots
- Wide operating temperature range
- Suitable for diverse industrial applications
9. Dell EMC PowerEdge XE2420
- Durable edge computing device designed for harsh environments
- Is capable of supporting up to two Intel Xeon Scalable processors
- Ruggedized chassis with extended temperature range support
- Flexible storage options including NVMe drives
- Ideal for edge deployments requiring high performance
10. OnLogic Karbon 700
- A sturdy edge computer built for dependable performance in harsh conditions
- Configurable I/O options
- Fanless cooling design
- Functions smoothly with both Windows and Linux operating systems
- Perfect for applications involving industrial IoT and edge AI
These edge computers provide various features to meet different edge computing demands, including AI acceleration and robust designs for industrial settings. The optimal choice is determined by the particular requirements of the edge application.
Edge Computers in Various Industries
Edge computers are finding applications across numerous industries:
1. Manufacturing
- Real-time quality control
- Predictive maintenance
- Supply chain optimization
2. Healthcare
- Remote patient monitoring
- Medical imaging analysis
- Telemedicine applications
3. Retail
- Intelligent video analytics
- Personalized shopping experiences
- Inventory management
4. Smart Cities
- Traffic management
- Public safety and surveillance
- Energy optimization
5. Agriculture
- Precision farming
- Crop monitoring
- Automated irrigation systems
6. Transportation
- Autonomous vehicles
- Fleet management
- Predictive maintenance for vehicles
Edge Computing vs. Cloud Computing
Although edge and cloud computing are frequently viewed as opposing models, they are increasingly being utilized in ways that complement each other. Here’s a comparison of key aspects:
| Aspect | Edge Computing | Cloud Computing |
| Data Processing Location | Near data source | Centralized data centers |
| Latency | Low | Higher |
| Bandwidth Usage | Reduced | Higher |
| Scalability | Limited by local resources | Highly scalable |
| Cost Structure | Higher upfront costs, lower ongoing | Lower upfront, pay-as-you-go |
| Reliability | Can operate independently | Depends on internet connectivity |
| Security | Data stays local | Centralized data storage |
| Maintenance | Requires on-site maintenance | Managed by service provider |
Many modern architectures leverage both edge and cloud computing to create powerful, flexible systems:
- Edge devices handle real-time processing and decision-making
- Cloud provides long-term storage, advanced analytics, and model training
- Edge-cloud collaboration optimizes overall system performance and efficiency
Challenges and Limitations of Edge Computing
Although edge computing provides many advantages, it also presents its own unique challenges:
1. Hardware Constraints
- Limited processing power relative to cloud data centers
- Storage capacity limitations
- Power consumption and heat dissipation issues
2. Security and Privacy
- Increased attack surface due to distributed nature
- Physical security risks for remote devices
- Ensuring data privacy and regulatory compliance
3. Standardization and Interoperability
- Lack of universal standards
- Compatibility issues between different vendors’ solutions
- Integration challenges with existing IT infrastructure
4. Network Reliability
- Dependence on reliable network connections
- Handling intermittent connectivity in remote deployments
- Ensuring data consistency across distributed nodes
5. Management and Orchestration
- Ensuring consistent software updates and patches
- The difficulty of managing an extensive network of distributed devices
- Monitoring and troubleshooting geographically dispersed infrastructure
6. Cost Considerations
- High initial investment for hardware deployment
- Ongoing maintenance and replacement costs
- Potential redundancy costs for high availability
7. Scalability
- Limitations in scaling compute resources at individual locations
- Complexity in managing data consistency as the number of nodes grows
8. Edge-Based Data Analytics and AI
- Limited resources for running complex AI models
- Challenges in updating and maintaining AI models across distributed nodes
9. Skill Gap
- Shortage of professionals with expertise in edge computing technologies
- Need for cross-disciplinary skills
10. Regulatory Compliance
- Varying data protection and privacy regulations across regions
- Auditing and reporting complexities for geographically dispersed systems
Addressing Edge Computing Challenges
To overcome these challenges, organizations can:
- Embrace a hybrid strategy that integrates both edge and cloud computing
- Implement edge-specific security measures
- Participate in standardization efforts
- Develop resilient architectures that can operate autonomously
- Leverage advanced management and orchestration tools
- Conduct a thorough cost-benefit analysis before implementation
- Design for scalability using modular architectures
- Optimize edge AI through model compression and specialized frameworks
- Allocate resources for training and skill enhancement for IT personnel
10. Stay informed about evolving regulations and design with compliance in mind
Future Trends in Edge Computing
The outlook for edge computing is highly promising, with several trends shaping its evolution:
1. 5G Integration: The rollout of 5G networks will enhance edge computing capabilities, enabling more responsive and data-intensive applications.
2. AI at the Edge: More sophisticated AI models will run directly on edge devices, enabling intelligent and autonomous systems.
3. Edge-Cloud Continuum: The distinction between edge and cloud computing will become less defined, leading to a smooth integration of computing resources.
4. IoT Expansion: The growing number of IoT devices will accelerate the adoption of edge computing.
5. Sustainability: Edge computing will be crucial in optimizing resource usage and reducing energy consumption.
6. New Use Cases: Innovative applications like augmented reality, autonomous vehicles, and personalized healthcare will emerge.
7. Standardization: Efforts towards standardization will accelerate, improving interoperability and integration.
Choosing the Right Edge Computer
When selecting an edge computer, consider the following factors:
1. Performance Requirements
- CPU and GPU capabilities
- Memory and storage needs
- AI acceleration requirements
2. Environmental Conditions
- Operating temperature range
- Dust and moisture resistance
- Vibration and shock tolerance
3. Connectivity Options
- Ethernet, Wi-Fi, and cellular capabilities
- Support for industrial protocols
4. Power Constraints
- Energy efficiency
- Support for wide input voltage ranges
5. Security Features
- Hardware-based security options
- Encryption capabilities
- Secure boot and trusted execution
6. Scalability and Expandability
- Modular design options
- Expansion slots and interfaces
7. Software Ecosystem
- Operating system support
- Compatibility with edge computing frameworks
- Development tools and SDKs
8. Total Cost of Ownership
- Initial purchase cost
- Operational and maintenance costs
- Lifespan and upgrade options
9. Vendor Support and Ecosystem
- Technical support quality
- Availability of documentation and resources
- Partner ecosystem for solutions and integrations
10. Compliance and Certifications
- Industry-specific certifications
- Regulatory compliance features
Case Studies: Successful Edge Computer Implementations
1. Manufacturing: Predictive Maintenance
- Implemented sensors and edge computers to monitor equipment health
- Achieved a 35% decrease in unplanned downtime
- Realized $2 million annual savings in maintenance costs
2. Healthcare: Remote Patient Monitoring
- Utilized edge computers alongside wearable devices for managing chronic conditions
- Reduced hospital readmissions by 40%
- Improved quality of life for patients through early intervention
3. Retail: Intelligent Video Analytics
- Installed edge computers with GPU acceleration for real-time video processing
- Boosted sales by 15% through improved product placement
- Reduced checkout wait times by 30%
4. Smart City: Intelligent Traffic Management
- Implemented edge computing for real-time traffic optimization
- Reduced average commute times by 20%
- Improved emergency response times by 30%
5. Agriculture: Precision Farming
- Deployed edge computers on agricultural equipment for real-time data processing
- Increased crop yields by 25%
- Reduced water usage by 30%
These case studies showcase the concrete advantages of edge computing in a range of industries., highlighting efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and overall performance improvements.
FAQs About Edge Computers
What exactly is an edge computer?
An edge computer is a specialized device intended for processing data near its source. It is tailored for low latency and real-time processing in environments with limited resources.
How do edge computers differ from regular PCs or servers?
Edge computers are typically more rugged, energy-efficient, and designed for specific edge computing tasks. They often have specialized hardware for AI acceleration and are built to operate in harsh environments.
What are the main benefits of using edge computers?
The primary benefits include reduced latency, improved privacy and security, bandwidth optimization, and the ability to operate in environments with limited connectivity.
Are edge computers secure?
Edge computers can be highly secure when properly implemented, often including hardware-based security features and the ability to process sensitive data locally.
Can edge computers work without an internet connection?
Many edge computers are designed to operate autonomously without a constant internet connection, processing data and making decisions locally.
How do edge computers handle AI and machine learning tasks?
Many modern edge computers are equipped with specialized hardware, such as GPUs or AI accelerators, to handle machine learning inference tasks efficiently.
What’s the relationship between edge computing and 5G?
Edge computing and 5G are complementary technologies. 5G provides high-speed, low-latency connectivity, enabling more powerful edge computing applications.
Conclusion: The Future of Edge Computing
Edge computing and edge computers represent a significant leap forward in our real-time ability to process and act on data. As we move into an increasingly connected and data-driven future, edge computing will be crucial in shaping how we interact with and leverage technology across all aspects of our lives and businesses.
Key Takeaways
- Edge computing enhances cloud computing, forming a more flexible and efficient data processing ecosystem.
- The best edge computers offer a balance of performance, energy efficiency, ruggedness, and security features.
- Successful implementation requires careful consideration of specific use cases and environmental factors.
- While challenges exist, ongoing innovations are addressing many limitations.
- The future of edge computing is bright, with 5G integration, AI advancements, and new use cases on the horizon.
As companies aim to harness the benefits of edge computing, it’s important to stay updated on new technologies, thoroughly evaluate specific needs, and think about a gradual adoption strategy. By embracing edge computing and navigating its challenges effectively, organizations can unlock new opportunities and drive meaningful change in their respective fields.
The evolution of edge computers continues to push the boundaries of what’s possible in distributed computing, promising a future where intelligent, real-time decision-making becomes the norm across industries and applications.